Blood DNA Extraction Using Spin Column: A Simple and Efficient Method
DNA extraction is a fundamental step in various molecular biology applications, including diagnostics, forensics, and research. One common source of DNA is blood, and spin column extraction has become a popular method for isolating DNA from blood samples due to its simplicity, speed, and high yield.
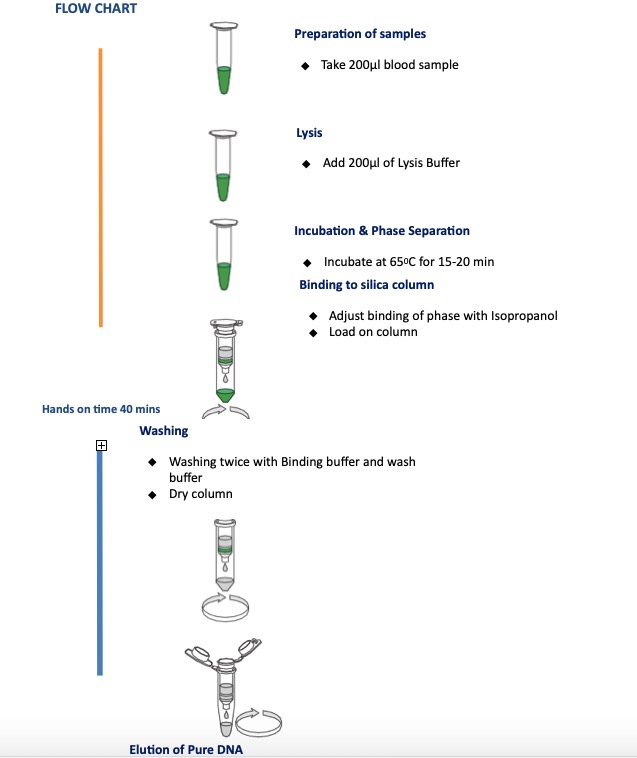
How Spin Column Extraction Works
- Cell Lysis: The first step involves breaking open the blood cells to release their contents, including DNA. This is typically achieved using a lysis buffer containing detergents and enzymes.
- Binding: A high-salt buffer is then added to the lysate, creating conditions that promote DNA binding to the silica membrane within the spin column.
- Washing: The column is washed with ethanol-based solutions to remove impurities, such as proteins and salts, while the DNA remains bound to the silica membrane.
- Elution: Finally, a low-salt buffer or water is used to elute the purified DNA from the column.
Advantages of Spin Column Extraction
- Ease of Use: The procedure is straightforward and can be performed with minimal training.
- Speed: The entire process can be completed in less than an hour.
- High Yield: Spin columns typically yield high amounts of pure DNA.
- Versatility: The method can be adapted for various sample types and DNA analysis applications.
Tips for Successful Spin Column Extraction
- Use Fresh Blood Samples: DNA degrades over time, so using fresh blood samples is crucial for obtaining high-quality DNA.
- Follow the Protocol Carefully: Each spin column kit may have slightly different instructions, so follow the provided protocol carefully.
- Avoid Cross-Contamination: Use clean gloves and pipettes to prevent contamination between samples.
Conclusion
Spin column extraction is a reliable and efficient method for isolating DNA from blood samples. Its simplicity, speed, and high yield make it a valuable tool for researchers and clinicians alike.
Lysis Buffer :
Blood DNA lysis buffer is a solution that breaks open blood cells to extract DNA. It’s used in molecular biology experiments to analyze DNA.
Binding Buffer :
A binding buffer is a reagent used to bind DNA to silica during DNA extraction. It helps to purify DNA from various samples, including blood, cells, and tissues. It contains Guanidine Hydrochloride and Nuclease free water
Washing buffer :
DNA Wash Buffer (80% ethanol, 20 mM NaCl, 2 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5)
Elution buffer :
(0.5 mM EDTA, 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 9.0 )
Blood gDNA Extraction Protocol
- Thoroughly mix the blood sample for at least 10 minutes in a rotisserie shaker at room temperature. If the blood has been frozen, thaw completely before mixing for 10 minutes.
- Take 200μl of fresh blood sample and transfer it to sterile 1.5 ml eppendorf tube.
- Note: The quality and quantity of DNA depend upon the age and storage of blood samples.
- Add 200μl of Lysis buffer and Mix thoroughly by vortexing.
- Incubate at 65°C for 15-20 minutes either on thermo mixer or water bath or dry bath. Briefly invert the tube once during incubation.
- Note: The lysate should be blackish red color at this point.
- After incubation add 100μl Isopropanol to the lysate. Mixed by inverting a tube 15- 20 times.
- Transfer entire lysate to the DNA spin column, and centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 2 mins. Discard the flow through liquid
- Repeat above step, until the entire sample has been processed and retain column for further processing.
- Place the column into the same collection tube. Add 500μl of Binding buffer. Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 2 min. discard the flow through.
- Place the column into same collection tube. Add 500μl of Wash buffer. Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1 min. discard the flow through.
- Place empty DNA spin column, with the lid open into the same collection tube and centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 2 min.
- Place the column into a new sterile 1.5 ml eppendorf tube, add 30 μl preheated Elution buffer. Incubate at room temperature for 5 min. (perform this step twice 30 μl + 30 μl = 60 μl)
- Centrifuge 10,000 rpm for 1 min to elute pure blood gDNA. The first elution normally yields 60-70 % of DNA bound. A second elution with another 30 μl buffer will yield another 20 % of the DNA.
- Note: Elution volume may vary as per downstream process
- Discard the Column, and save elute. Do not reuse binding columns or collection tubes.
For any inquiry , Please feel free to write me on :jayeshjblogs@gmail.com
You can also write me if you need DNA and RNA Spin columns
